3-Octave Modal Scale-Patterns
- H Kurt Richter
- Dec 1, 2024
- 2 min read
Standard 3-Octave Scale-Patterns by Mode
Most soloing and melody-making can be done effectively within a 2-octave span. But there may be times when a 3-octave span is desired. Here are some example 3-octave scales.
For advanced players, it is impressive to be able to do 3-octave scales very fast, picking each note, although the glissando technique is valid. Be able to do both. However, with 3-octave scales, glissandos you may wish to use at least one fret-finger to slid up ascending, or slid down descending, on the 1st through 4th strings, given the patterns shown below.
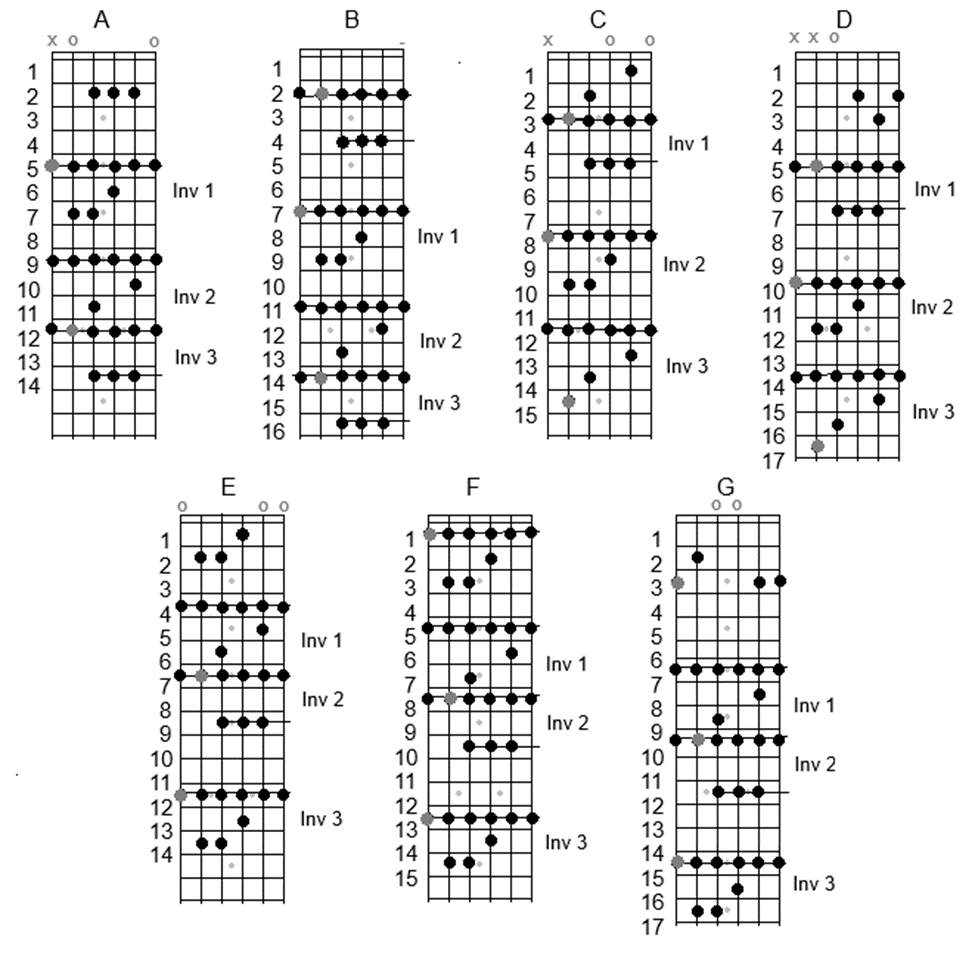
These are examples of the seven Modal Scale-Patterns covering three octaves each; one for each Mode. The lowest note is the root, and the highest note is the third octave of the root.
Fingering is up to the player, but I recommend using the pointer finger at the root, so you end up with the pinky at the third octave in an ascending run.
Within each pattern, if you do not wish to use all four fret-fingers on all but the 5th and 6th strings, you can slide up with the pinky, but slide down with the pointer, as desired. For instance, slide up with the pinky but down with the pointer on the 3rd and 4th strings, but use all four fret-fingers on the 1st and 2nd strings without sliding.
For learning each scale, and practicing to keep speed up after memorizing, the best method is to do each scale ascending followed immediately by descending. And do that as many times as can be tolerated in every learning/practice session (up to a hundred times each, for learning purposes). Once a scale is memorized, and can be played fast, it becomes easy to devise licks and melodies within it that do not require strict up/down runs.

The above examples use the G root on the 6th string at the 3rd fret, but the patterns can be played anywhere on the fretboard within any given 13-fret span. Thus, the root at the low E can be the open E on the 6th string, which means the A on the 5th string will be open as well. Otherwise, the highest pattern available on a 24-fret guitar will have its root as E-flat on the 6th string at the 11th fret. Guitars with fewer frets will be more limited. For instance, the highest such pattern on a 22-fret guitar will have its 6th-string root at the 9th fret.
Of course, you do not have to play the full pattern every time one is used. Yes, memorize the patterns, but employ them as you will. However, you will notice that the most impressive use of any given pattern is when you play it as a full scale run very fast, without making mistakes.

Comments